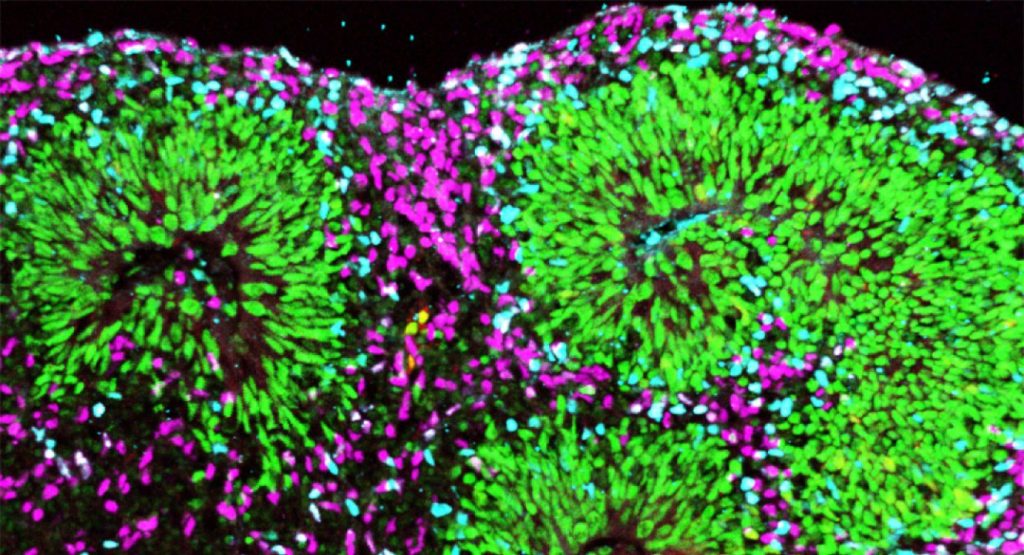
The quest to unravel the mysteries of human evolution has long been a focal point of scientific inquiry. Among the myriad traits that define humanity, the neocortex—a complex outer layer of the brain—is hailed as a hallmark of our cognitive prowess. In a groundbreaking study led by Dr. Mareike Albert at the Center for Regenerative Therapies Dresden (CRTD) of TUD Dresden University of Technology, a novel factor implicated in the expansion of the human neocortex has emerged. Published in the EMBO Journal, this research sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying our unique cognitive abilities and underscores the transformative potential of brain organoid technology.
The Neocortex: A Nexus of Human Cognition The neocortex stands as a testament to the evolutionary journey of the human brain. Across mammalian species, variations in neocortical size and complexity mirror divergent cognitive capacities. While all mammals possess a neocortex, humans and primates exhibit distinctive folding patterns that augment surface area and facilitate higher cognitive functions. Dr. Albert’s team embarked on a quest to decipher the molecular underpinnings driving this remarkable expansion of the human neocortex.
Unraveling Molecular Mysteries through Organoid Exploration Harnessing the power of 3D cell culture technology, the researchers embarked on a comparative analysis of developing brains in mice and humans. This innovative approach unveiled a pivotal factor—epiregulin—that is conspicuously absent in mice but prevalent in humans. By leveraging human stem cells to generate brain organoids, the team demonstrated epiregulin’s role in promoting the proliferation and expansion of neocortical stem cells. Through meticulous experimentation, they illuminated the nuanced interplay between molecular cues and neocortical development.
From Humans to Gorillas: Tracing Evolutionary Threads Driven by a quest for deeper insights, the researchers extended their investigations to include gorilla brain organoids—an endeavor aimed at elucidating the evolutionary continuum of epiregulin’s influence. Intriguingly, while epiregulin exerted a stimulatory effect on gorilla brain organoids, its impact on human counterparts was more nuanced. This divergence underscored the pivotal role of epiregulin dosage in modulating inter-species differences in neocortical expansion.
Implications for Human Evolution and Ethical Research The findings of this study transcend mere scientific curiosity, offering profound implications for our understanding of human uniqueness. By elucidating the molecular mechanisms underpinning neocortical expansion, researchers inch closer to unraveling the enigma of human cognition. Moreover, the ethical dimensions of this research are underscored by the utilization of non-invasive brain organoid technology—a paradigm shift that complements traditional animal studies while minimizing ethical concerns.
As humanity continues its quest to fathom the depths of its own origins, studies such as these serve as guiding beacons, illuminating the path toward enlightenment. Dr. Mareike Albert and her team have embarked on a journey of discovery—one that transcends disciplinary boundaries and illuminates the intricate tapestry of human evolution. Through their pioneering research, they beckon us to peer into the labyrinth of the human brain, where secrets of our past and keys to our future await discovery. In the realm of organoid exploration, a new frontier beckons—one where ethical inquiry converges with scientific advancement to unveil the mysteries of human uniqueness.