High cholesterol is a prevalent health concern affecting millions of people worldwide. Despite its widespread prevalence, many individuals remain unaware of the underlying causes and potential consequences of elevated cholesterol levels. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate mechanisms behind high cholesterol, explore the factors that contribute to its development, and discuss why managing cholesterol levels is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Understanding Cholesterol: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
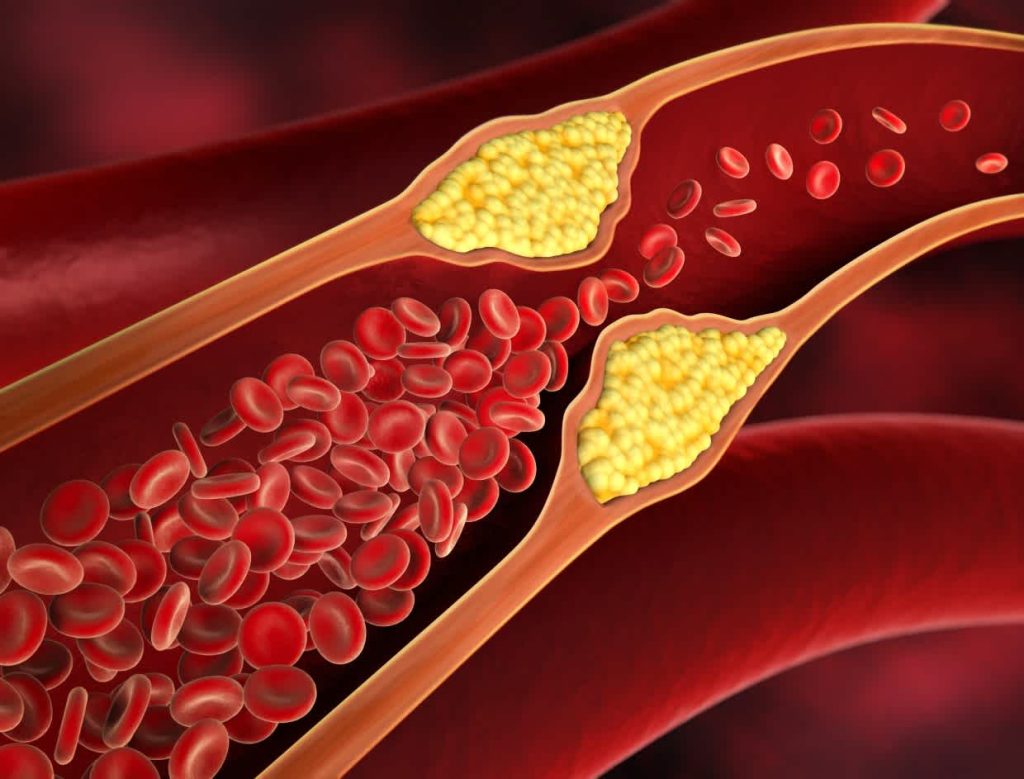
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in the blood and essential for various physiological functions in the body. While cholesterol is necessary for cell membrane structure, hormone production, and bile acid synthesis, excess cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and lead to plaque formation, narrowing of the blood vessels, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Cholesterol exists in two primary forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol transports cholesterol from the liver to the cells, where it can accumulate in the arteries and contribute to plaque buildup. In contrast, HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transport it back to the liver for excretion, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
What Causes High Cholesterol?
- Unhealthy Diet: One of the leading causes of high cholesterol is a diet high in saturated and trans fats, commonly found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, processed foods, and fried foods. Consuming excessive amounts of these unhealthy fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and regular exercise can contribute to high cholesterol levels by promoting weight gain, reducing HDL cholesterol levels, and impairing lipid metabolism. Regular exercise helps boost HDL cholesterol levels, improve circulation, and promote overall cardiovascular health.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence cholesterol levels and predispose individuals to familial hypercholesterolemia, a genetic disorder characterized by high LDL cholesterol levels from birth. People with a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular disease may be at increased risk and require closer monitoring and intervention to manage their cholesterol levels effectively.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is closely linked to elevated cholesterol levels and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Obesity can lead to insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome, all of which contribute to elevated LDL cholesterol levels and reduced HDL cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage blood vessels, increase inflammation, and contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries. Smoking is associated with lower HDL cholesterol levels and higher LDL cholesterol levels, making it a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- Age and Gender: Cholesterol levels tend to increase with age, particularly in women after menopause. Estrogen helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels in premenopausal women, but after menopause, cholesterol levels may rise as estrogen levels decline. Additionally, men typically have higher cholesterol levels than premenopausal women, but this difference narrows after menopause.
Why High Cholesterol Matters: The Consequences of Untreated Hypercholesterolemia
- Cardiovascular Disease: High cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, including coronary artery disease, heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Elevated LDL cholesterol levels contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and restricting blood flow to vital organs. Over time, plaque buildup can lead to atherosclerosis, heart disease, and life-threatening cardiovascular events.
- Hypertension: High cholesterol is often associated with high blood pressure, another significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Hypertension increases the workload on the heart, damages blood vessels, and accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis. Managing cholesterol levels is essential for preventing and managing hypertension and reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Diabetes: High cholesterol and diabetes often coexist and share common risk factors, including obesity, unhealthy diet, and sedentary lifestyle. People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, as elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and worsen lipid abnormalities. Managing cholesterol levels is an integral part of diabetes management and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors, including abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal lipid levels, that increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. High cholesterol is a key component of metabolic syndrome and requires comprehensive management to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Elevated cholesterol levels are associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, a condition characterized by excess fat accumulation in the liver. NAFLD can progress to more severe liver damage, including inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis, increasing the risk of liver failure and liver cancer. Managing cholesterol levels is essential for preventing and managing NAFLD and promoting liver health.
Managing High Cholesterol: Strategies for Prevention and Treatment
- Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet: Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet can help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve overall cardiovascular health. Limiting saturated and trans fats, cholesterol-rich foods, processed foods, and sugary beverages can reduce the risk of elevated cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity and aerobic exercise can help lower LDL cholesterol levels, raise HDL cholesterol levels, and improve overall lipid profile. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week to reap the cardiovascular benefits of regular physical activity.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help lower LDL cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Losing excess body weight, particularly abdominal fat, can lead to significant improvements in lipid levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. Tobacco smoke damages blood vessels, increases inflammation, and accelerates atherosclerosis, making it a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Seek support from healthcare professionals, smoking cessation programs, and support groups to quit smoking and improve your cardiovascular health.
- Medication Therapy: In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to lower cholesterol levels to the desired target. Medications such as statins, cholesterol absorption inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, and PCSK9 inhibitors may be prescribed to help lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual risk factors, medical history, and cholesterol levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, high cholesterol is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease and other serious health conditions, making it essential to understand the underlying causes and consequences of elevated cholesterol levels. By addressing modifiable risk factors such as unhealthy diet, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and poor cholesterol management, individuals can reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease and improve their overall health and well-being. Prioritizing heart-healthy habits, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation,
maintaining a healthy weight, and adhering to medication therapy when necessary, is crucial for managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
Furthermore, raising awareness about the importance of cholesterol management and debunking common misconceptions surrounding high cholesterol can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards better heart health. By fostering a culture of prevention, education, and collaboration between healthcare providers and patients, we can work together to combat the growing burden of cardiovascular disease and improve health outcomes for individuals worldwide.
Ultimately, the journey to better heart health begins with knowledge, awareness, and action. By understanding the causes of high cholesterol, recognizing its impact on health, and implementing evidence-based strategies for prevention and treatment, individuals can take control of their cardiovascular health and live longer, healthier lives.
Remember, managing high cholesterol is not just about lowering numbers on a lab report—it’s about protecting your heart, preventing cardiovascular disease, and enjoying a higher quality of life. Whether you’re making dietary changes, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, or exploring medication options, every step you take towards better cholesterol management brings you closer to a healthier, happier future.
In conclusion, let’s continue to raise awareness, dispel myths, and promote heart-healthy habits in our communities. Together, we can make a meaningful impact on the prevention and management of high cholesterol and ultimately reduce the burden of cardiovascular disease for generations to come.
Read More: Scientists Reveal New Findings About Older Adults Who Take Vitamin D